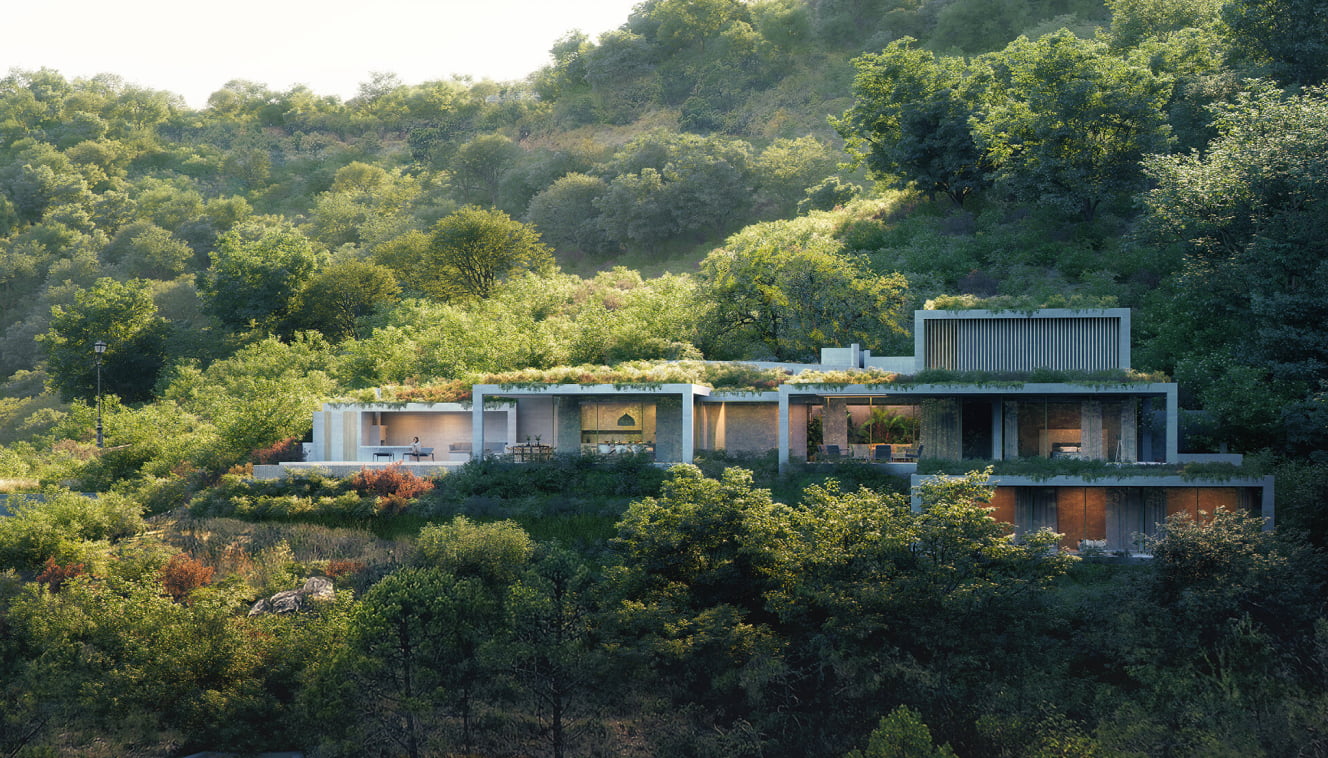
In the world of architecture and design, 3D visualization has become a crucial tool for presenting projects and conveying design ideas to clients. Architectural 3D visualization services have the power to bring a design to life, allowing the viewer to fully understand the layout, aesthetics, and functionality of a space. As technology advances, so do the rendering techniques used in architectural visualization. In this blog post, we will discuss five popular rendering techniques that have shaped the industry and are commonly used to create stunning visual representations of architectural designs.

Ray Tracing
Ray tracing is one of the most popular rendering techniques used in architectural 3D visualization services. It works by simulating the way light travels in the real world, tracing the path of individual rays of light as they interact with surfaces and materials. This allows for accurate reflections, refractions, and global illumination, resulting in photorealistic images.
Ray tracing can be computationally intensive, as it requires calculating the behavior of millions of light rays. However, recent advancements in computer hardware and rendering software have made it more accessible to a wider range of users. Many architectural visualization studios now utilize ray tracing to create high-quality still images, animations, and interactive experiences.
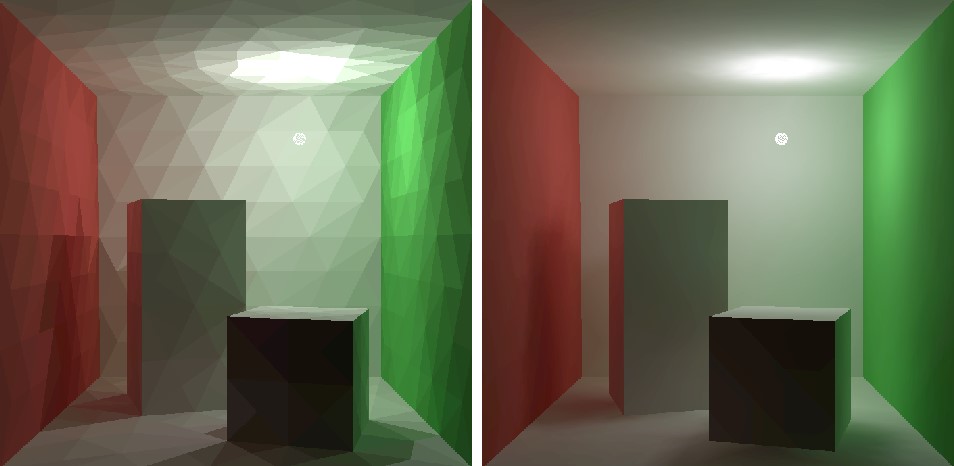

2. Radiosity
Radiosity is another popular technique used in architectural visualization to simulate the complex behavior of light. Unlike ray tracing, which focuses on the direct interaction between light and surfaces, radiosity considers the indirect illumination caused by light bouncing off surfaces. This results in more realistic and natural-looking lighting, especially in scenes with multiple light sources and complex geometries.
The radiosity method is based on the principle of energy conservation, where the total amount of energy in a scene remains constant as it is transferred from one surface to another. Radiosity calculations can be time-consuming, but many rendering software packages offer precomputed radiosity solutions, allowing for faster rendering times while still maintaining accurate lighting.
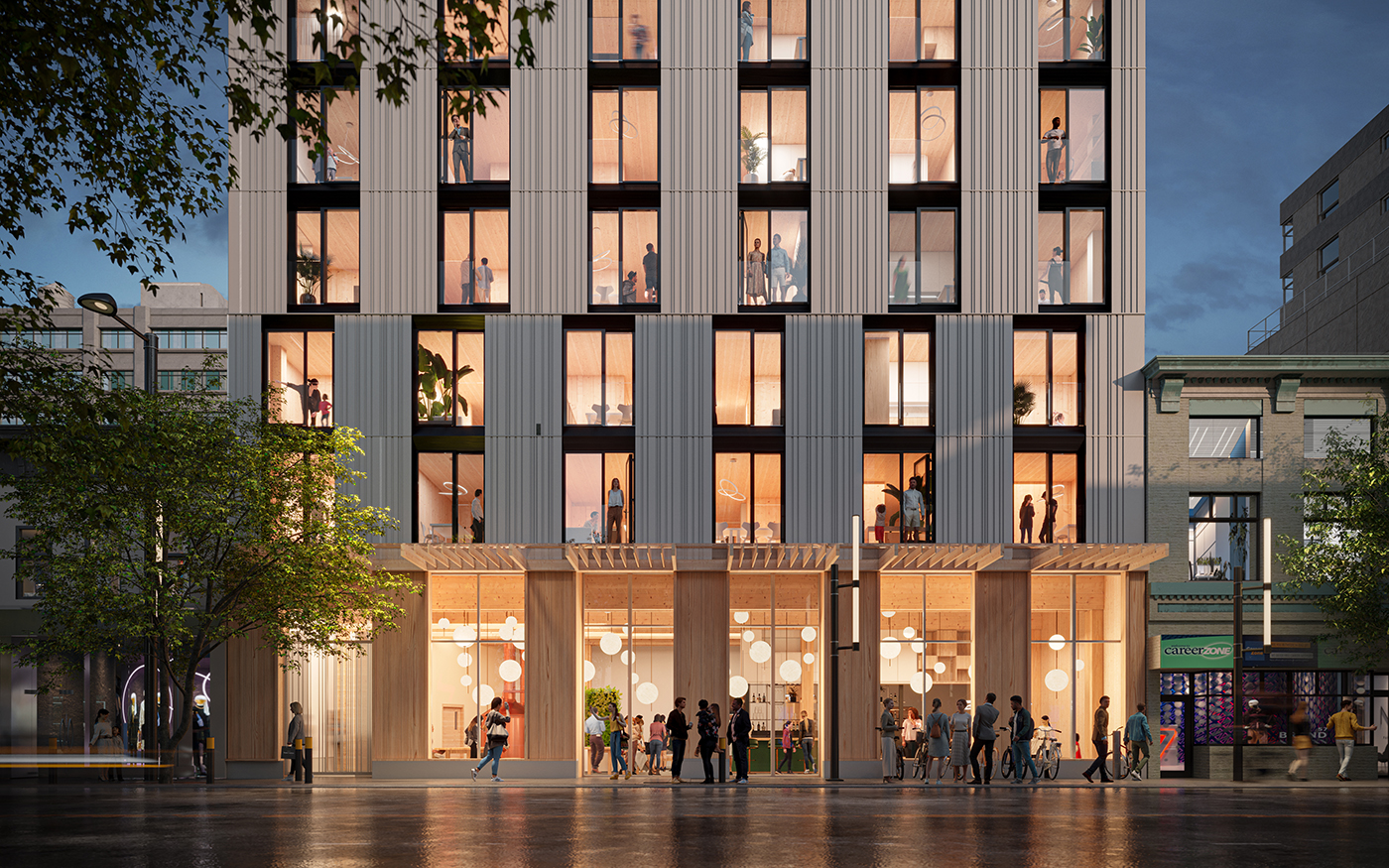

3. Real-time Rendering
Real-time rendering is a technique used in architectural visualization to create interactive experiences and walkthroughs. Unlike traditional offline rendering methods, real-time rendering generates images at a rapid pace, allowing the user to navigate and explore a 3D environment in real-time. This is made possible through the use of powerful graphics processing units (GPUs) and optimized rendering algorithms.
Real-time rendering is particularly useful for architectural presentations and client meetings, as it allows the viewer to fully immerse themselves in the environment and gain a better understanding of the space. With advancements in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technology, real-time rendering is becoming an increasingly important tool in the architectural visualization toolkit.

4. Physically Based Rendering (PBR)
Physically based rendering (PBR) is a modern rendering technique that aims to create more realistic and consistent results by simulating the physical properties of materials and light. PBR relies on complex mathematical models and algorithms to accurately represent the way light interacts with different materials, such as metals, plastics, and fabrics.
PBR has become increasingly popular in architectural visualization due to its ability to produce photorealistic images with accurate colors, shadows, and reflections. Many rendering software packages now support PBR workflows, allowing artists to create stunning visualizations with a high level of detail and realism.
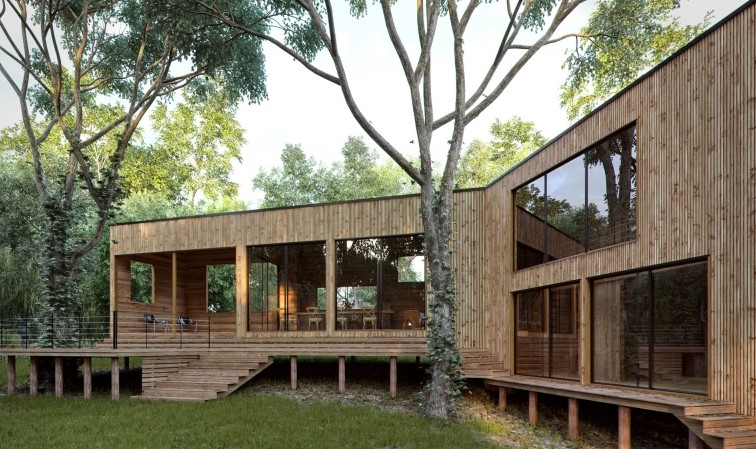

5. Hybrid Rendering
As the name suggests, hybrid rendering combines elements of different rendering techniques to achieve the best possible results. For instance, a hybrid renderer might use ray tracing for reflections and refractions, radiosity for global illumination, and real-time rendering for interactive elements. By leveraging the strengths of each technique, hybrid rendering can produce high-quality images and animations while minimizing computation time and resource usage.
Hybrid rendering is becoming increasingly common in architectural visualization, as it allows artists to create a wide range of visual styles and achieve a high level of detail and realism. By selecting the appropriate combination of rendering techniques, studios can tailor their visualization services to meet the unique needs and preferences of each client.
In conclusion, the architectural 3D visualization industry is constantly evolving, with new rendering techniques and technologies emerging regularly. By staying informed about the latest developments and selecting the appropriate rendering methods, visualization studios can create stunning, lifelike representations of architectural designs that captivate and inspire clients. From ray tracing and radiosity to real-time rendering and physically based rendering, the possibilities for creating striking visualizations are virtually limitless.